The semen analysis is the first diagnostic test to be performed on the male of a couple in the context of an infertility study. It is an analysis of a punctual semen sample. In it, the number of spermatozoa per milliliter of ejaculate (concentration), its shape (morphology), and its mobility are studied. A series of biochemical and physical parameters are also analyzed.
Spermatozoa are very sensitive to physical and chemical changes. Thus, in order to compare the results of the semen analysis with the normal parameters, it is necessary to standardize the sample collection conditions: days of abstinence, time from collection to processing of the sample, absence of lubricants, condoms, or other exogenous agents, etc.
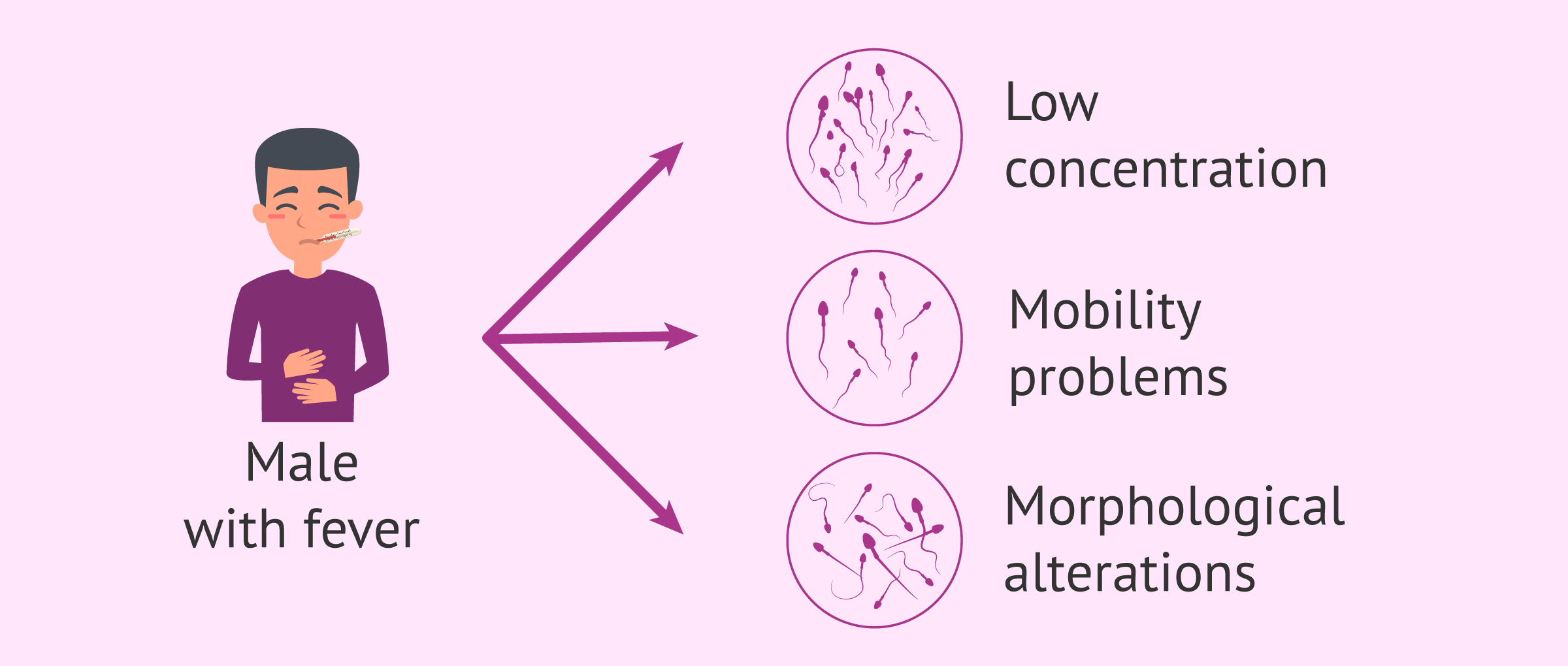
Among the factors that can affect the results of the semen analysis is "heat". In order to produce and nourish sperm, the temperature of the testes must remain approximately one/two degrees lower than that of the rest of the body. Therefore, the male testes are located in the scrotum, anatomically outside the abdomen and, the scrotum can move the testes to maintain this delicate balance: in warm temperatures, the testes can be kept further away from the body and, in cold temperatures, the testes will move closer. However, if the testes cannot maintain this ideal temperature, as can occur during fever, sperm production is hampered or may even cease for a short time. Fever has been associated with decreased sperm count, motility, and morphology.
It is important to understand that the process of spermatogenesis (sperm production process) in the male is continuous. That means that cycles are constantly being initiated. And, each complete cycle of spermatogenesis lasts approximately 75-90 days. It is also known that the stages of sperm production most affected by temperature are those that occur 30-60 days prior to ejaculation.
Because the complete cycle of spermatogenesis is 90 days, when a high fever episode has occurred, it can affect sperm quality for the next 3 months. After 3 months, there will be no sperm left in the testicles that have undergone the temperature increase.
On the other hand, given that the cycles are continuous, and that the stages most vulnerable to the rise in temperature are the 30-60 days prior to ejaculation, normally 6 weeks after the episode of temperature rise, the result of the semen analysis is usually normal.
For this reason, whenever a semen analysis is performed, it is recommended to wait 6 weeks after a febrile episode. And, patients are advised to notify their physician of fever episodes in the last 2-3 months.
In any case, due to the sensitivity of spermatozoa to exogenous changes, we should always repeat this test to confirm the results of an altered semen analysis. And, given the above, the most correct recommendation would be to repeat it 3 months after the first semen analysis (complete spermatogenesis cycle), but in practice, it is usually repeated at 5-6 weeks for the convenience of the patients and because, being continuous cycles, with this time we can already see significant changes if the alteration of the semen analysis has been due to an external agent.
