Intrauterine fetal death, also called fetal stillbirth, is the death of the fetus before expulsion or extraction at birth and, according to the World Health Organization (WHO), is independent of the duration of pregnancy.
However, in general, antepartum fetal death is considered to occur after the 20th week of gestation. In addition, late fetal death is also referred to if it occurs after the 28th week.
After being born, the dead fetus is called stillbirth o fetus cross.
Provided below is an index with the 7 points we are going to expand on in this article.
- 1.
- 1.1.
- 1.2.
- 1.3.
- 2.
- 3.
- 4.
- 4.1.
- 4.2.
- 4.3.
- 4.4.
- 4.5.
- 5.
- 6.
- 7.
Causes
There are multitude of causes that can explain the death of the fetus in utero, although they are difficult to determine.
The origins of fetal death may be maternal, fetal, or placental related. In some cases, it will be possible to prevent them in advance and act in time to prevent the death of the baby.
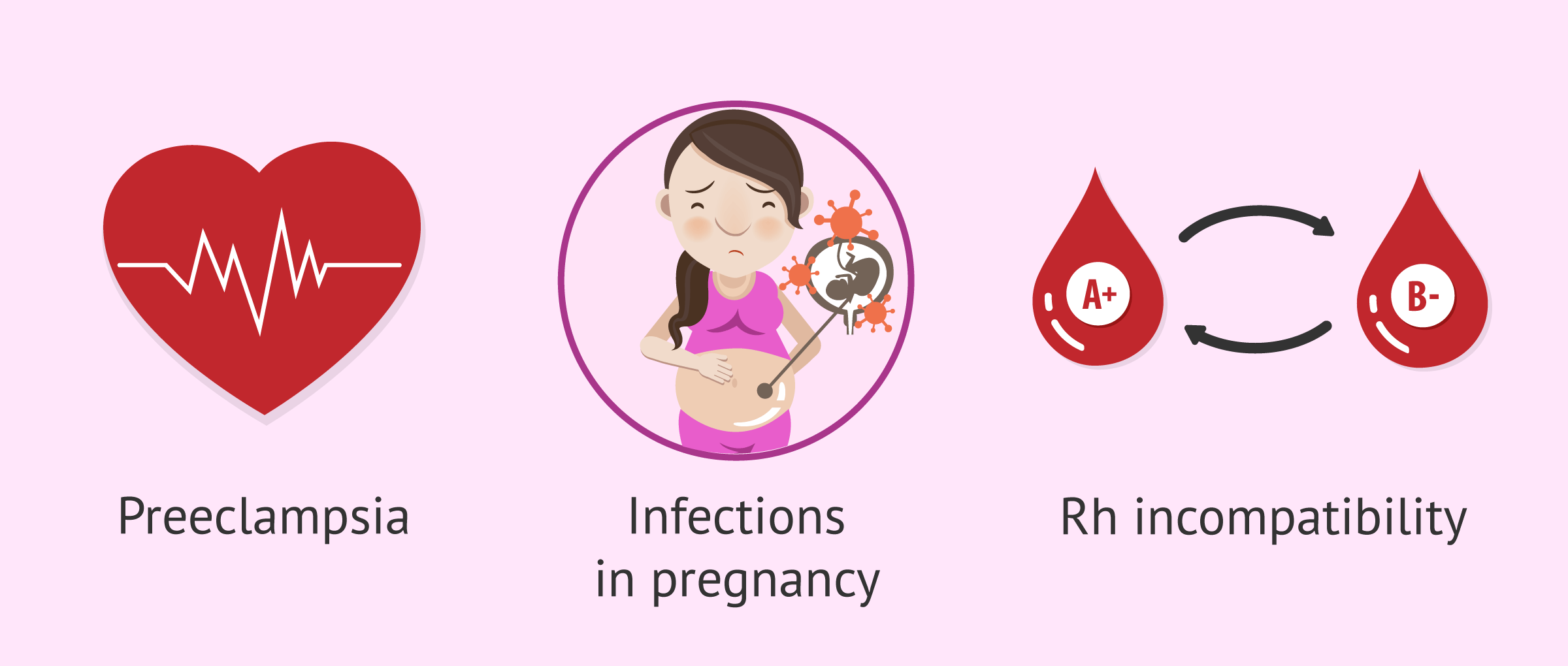
Maternal causes
The problems that can lead to antepartum fetal death related to the mother are as follows:
- Chronic diseases: lupus, diabetes mellitus, antiphospholipid antibodies, high blood pressure, etc.
- Prolonged pregnancy lasting more than 42 weeks.
- Infections during pregnancy: listeriosis, rubella or toxoplasmosis.
- Preeclampsia.
- Rh incompatibility: the Rh of the maternal blood is different from the Rh of the baby.
- Uterine rupture.
- Death of the mother.
It is important for the woman to know if she has any pre-pregnancy disease in order to take the necessary measures and/or decide if she wants to carry out the pregnancy.
In addition, there are some factors that increase the risk of fetal death: smoking, alcohol, drugs, advanced maternal age, malnutrition, etc. It is very important for a woman to lead a healthy lifestyle throughout her pregnancy.
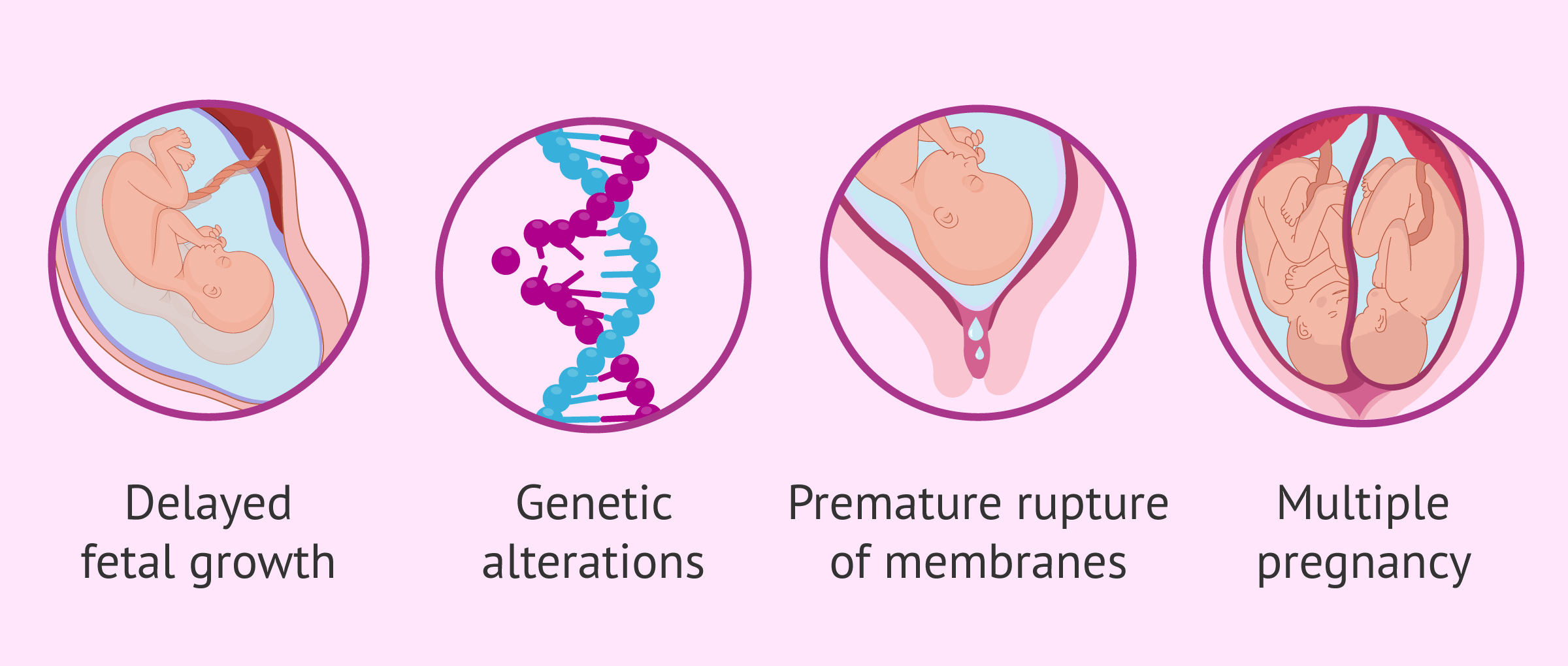
Fetal causes
It is possible that some alterations in the fetus during gestation are responsible for the death of the fetus:
- Intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR): the fetus does not grow at the right rate and they are smaller.
- Genetic and chromosomal alterations.
- Congenital malformations.
- Alterations in the amniotic fluid: oligohydramnios and polyhydramnios.
- Multiple pregnancy: circulatory imbalance to the benefit of one baby and detriment of the other.
- Premature rupture of membranes.
Placental causes
Among the causes related to the placenta, we can name the following:
- Umbilical cord pathology: circular, knots, twists and ruptures.
- Placental abruption
- Placenta previa.
- Severe aging of the placenta.
- Vasa previa: the fetal blood vessels are not protected by the cord, they can tear and cause bleeding in the baby.
Many of these placental pathologies cause significant hemorrhage, which prevents the fetus from receiving sufficient oxygen and nutrients, ultimately resulting in death.
Diagnostic tests
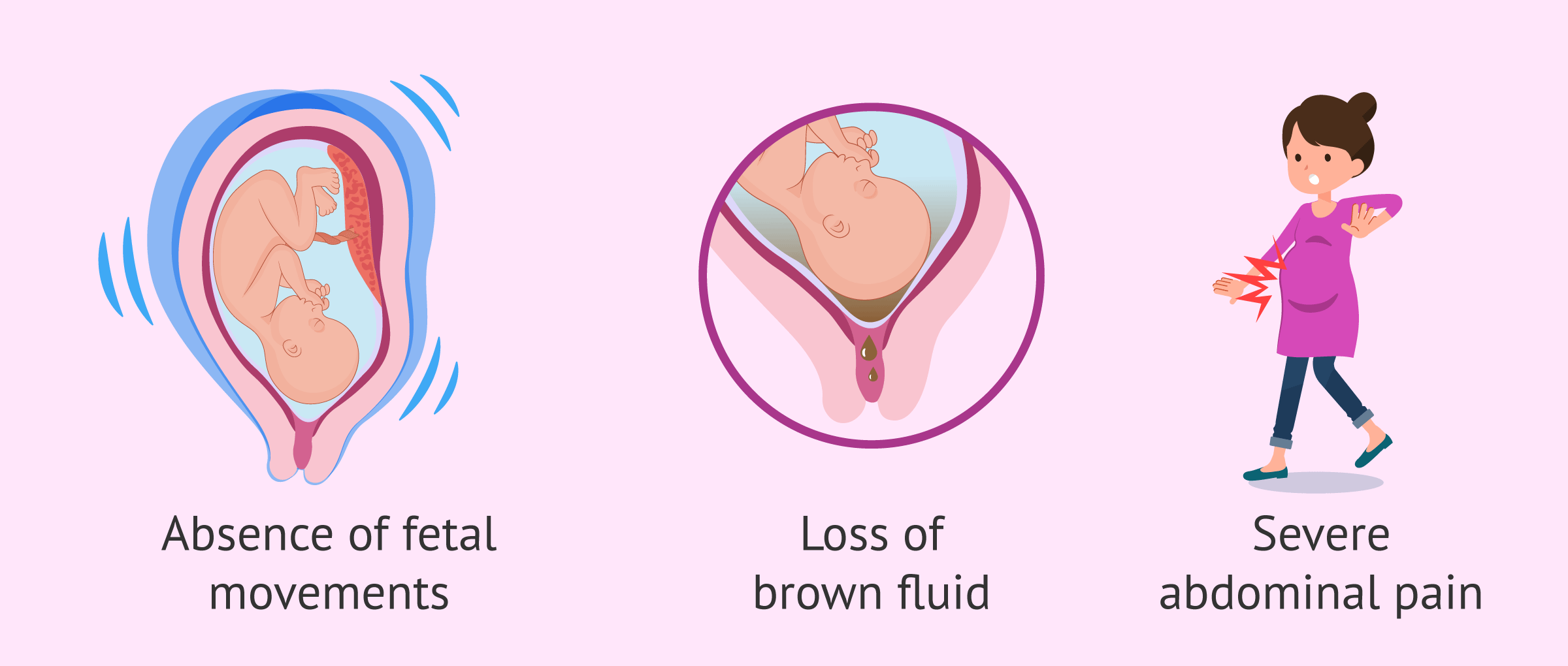
Detecting fetal death isn´t easy However, it is important for the mother to watch for any signs that something is wrong with the pregnancy. Possible symptoms of having a dead baby in utero are as follows:
- Absence of fetal movements
- Brown leaking of amniotic fluid
- The uterus does not grow
- Disappearance of elasticity and firmness of the fetal parts to palpation
- Severe abdominal pain
- Vaginal bleeding
If you experience these symptoms, it is very important to go to the gynecologist as soon as possible and check if the fetus is still alive. Through an abdominal ultrasound, the gynecologist will confirm if there is a heartbeat.
In addition, if the fetal death has occurred some time ago, all fetal structures and the placenta will be carefully examined to find a possible cause. It is important to check for overlapping of the cranial sutures, thickening of the scalp (halo scalp ring), pleural and peritoneal effusion, fetal edema, etc.
Eighty-six percent of fetal deaths occur before delivery, while 14% occur during delivery.
How to deal with fetal death?
Fetal death is one of the obstetric problems with the greatest psychological implications for both the couple and the healthcare personnel.
Having to face the loss of a baby before birth is a particularly hard and difficult time for expectant parents, who look forward to the arrival of a child throughout their pregnancy.
Support between both partners is essential to avoid states of anxiety and depression.
Therefore, it is important for the physician to report the fetal death in the presence of both parents or, if this is not possible, for the mother to be in the company of a family member or friend.
It will then be reported that a definitive diagnosis of the cause can only be established by fetal autopsy, although this is not always conclusive. It is important to consider this option in order to avoid similar complications in a future pregnancy.
Finally, after giving birth to a stillborn baby, many psychologists recommend that parents see the baby to help them accept the loss and get over it more quickly.
In this case, the health personnel will prepare the baby, clean him and wrap him in a blanket, so that he appears to be asleep.
Regardless, the ultimate decision as to whether or not they want to see the lifeless baby is up to the parents alone.
FAQs from users
What are the signs of intrauterine fetal death, and could it be prevented?
Absence of fetal movements for more than 4 hours despite stimulation.
It is recommended to go to the emergency room for an ultrasound.
It cannot be avoided, since in many cases it happens even with a controlled pregnancy and normal laboratory tests.
What happens after diagnosing a cross fetus?
It is possible to spontaneously expel the baby in preterm labor 2 to 3 weeks after fetal death. However, it is advisable to induce labor in order to avoid possible complications for the mother, such as hemorrhage or infection.
In addition, retaining a stillborn fetus after diagnosis may lead to further emotional problems for the parents.
Is it possible to prevent intrauterine fetal death?
On certain occasions, it is possible that the woman feels that something is not right and alerts the doctor to find a solution. If there is indeed fetal distress that could put the pregnancy at risk, it is possible to take measures such as scheduling a cesarean delivery.
These are some recommendations for the mother to prevent stillbirth:
- Count the daily kicks of the baby from week 26. It is normal to feel at least 10 kicks a day. If the mother notices that the fetus is less active, this would be a red flag.
- Stop tobacco and alcohol from the moment a woman knows she is pregnant.
- If the woman has already had a cross fetus in the past, it is advisable to monitor this pregnancy more carefully, make more visits to the gynecologist, more ultrasounds, rest, etc.
Can anything happen to me if I have a dead baby in my womb?
If there is rupture of the gestational sac membranes, a bacterial infection may occur, leading to major complications. Depending on the cause, it is also possible that there may be a problem in the mother's blood (coagulopathy) or that there may be major hemorrhages. Therefore, the first thing the doctor will do is to evaluate the medical situation of the pregnant woman and then make the most appropriate decision to remove the fetus.
What happens when one of the twins dies in utero?
First of all, you have to assess the situation and act in such a way that the other baby is not in danger. It all depends on the length of the pregnancy and whether or not the twins share the placenta.
Generally, it is not advisable to induce labor unless it is strictly necessary. If it is still too early to give birth, it is best to continue with the pregnancy so that the living baby has more time and can develop well. When the time comes, both babies will be born at the same time.
Recommended readings
You may be in an at-risk pregnancy situation. If you want to know how to deal with it, we recommend you to read the following post: High-risk pregnancy.
Women who have suffered an antepartum stillbirth will also have to deliver the baby to expel it from the body. To learn more about what it's like to go into labor, you can continue reading here: Preparation and types of childbirth.
We make a great effort to provide you with the highest quality information.
🙏 Please share this article if you liked it. 💜💜 You help us continue!
References
FAQs from users: 'What are the signs of intrauterine fetal death, and could it be prevented?', 'What happens after diagnosing a cross fetus?', 'Is it possible to prevent intrauterine fetal death?', 'Can anything happen to me if I have a dead baby in my womb?' and 'What happens when one of the twins dies in utero?'.
Authors and contributors
More information about Cristina Algarra Goosman





Hi, I am 32 weeks and I am very afraid that this will happen to my son. A few months ago we had a scare with his heart rate and the doctor has told me that I have to rest. Is there anything I can do to make sure he is ok?
Hi KhloeStar,
When facing a risky pregnancy the most important thing is to follow the medical recommendations. That is to say, in your case, keep resting and avoid sudden movements or actions.
You can do weekly checkups to make sure that the baby’s heart is fine. The baby’s movements as well as the absence of pain or strange sensations are things to keep in mind.
If you notice any strange symptoms, don’t hesitate to go to the emergency room so they can confirm that your baby is doing well.
I hope I have helped you.
Best regards.
Hello, I had a stillbirth at 28 weeks pregnant, we were devastated and I can´t help but think that there was something I could have done to prevent it… We are trying to conceive our little rainbow baby but I´m afraid this will happen again.
Hi Olivia89,
I am so sorry you had to go through this. A stillbirth is a hard process that unfortunately many women and couples go through.
Trying to achieve pregnancy after death is something to do with caution, it is important to identify if possible what the cause of death was and if anything can be done to minimize the risks in this new pregnancy. Medical control will play an important role in this new pregnancy since it will become a risk pregnancy.
I recommend that you read this article: How can you manage a high-risk pregnancy?
I hope I have helped you.
Best regards.