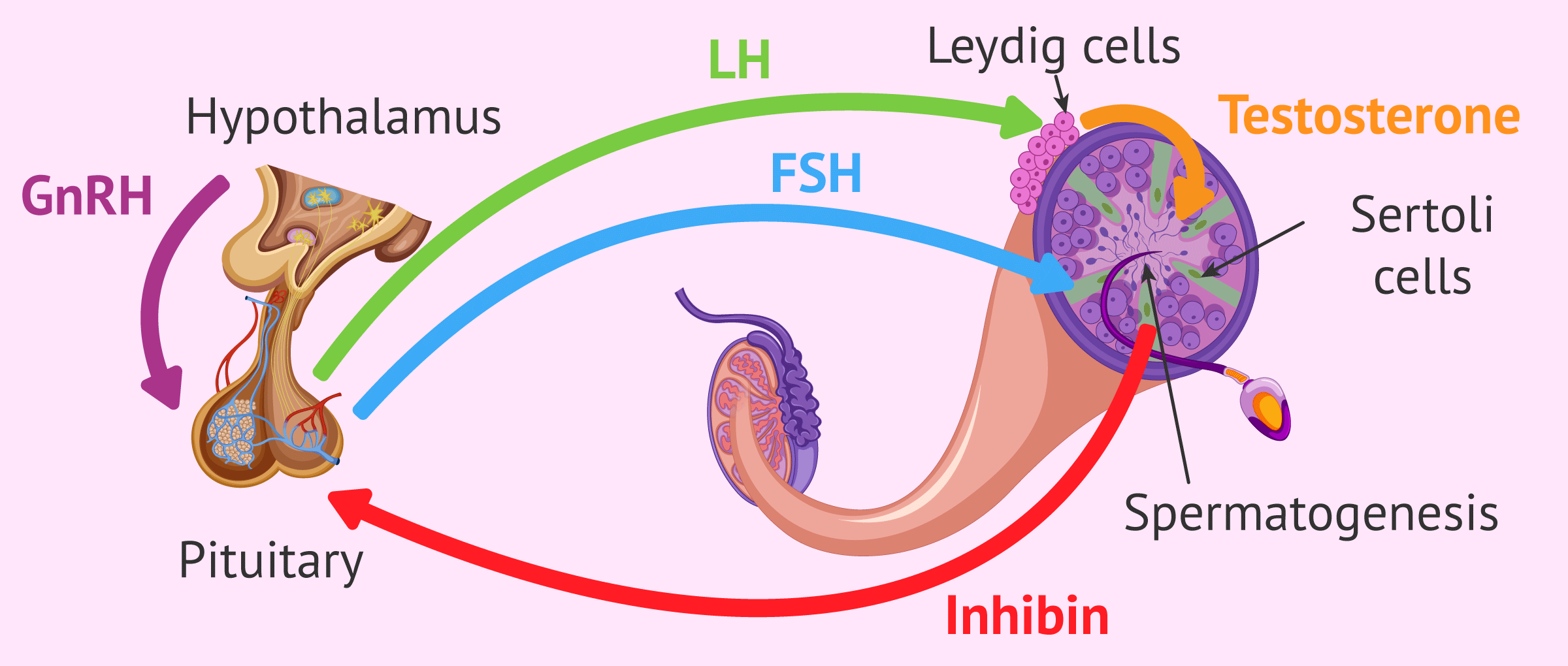
The hormones involved in the control of spermatogenesis are the following:
- Testosterone
- is secreted by Leydig cells of the testis. One of its functions in this process is to activate genes that promote the differentiation of spermatogonia.
- FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone)
- is secreted by the pituitary gland and acts on the testicle, in the Sertoli cells. These are responsible for nourishing the sperm and promoting their development and maturation.
- LH (luteinizing hormone)
- is also secreted by the pituitary gland. Its main function is to activate the release of testosterone in the Leydig cells.
- Inhibin
- is released by Sertoli cells. It inhibits the release of FSH in the pituitary gland and therefore stops spermatogenesis through negative feedback.
Read the full article on: How are spermatozoa formed? – Phases of spermatogenesis ( 46).
By Manuel Aparicio Caballero M.D., M.Sc. (gynecologist), Marta Barranquero Gómez B.Sc., M.Sc. (embryologist), Rebeca Reus BSc, MSc (embryologist) and Cristina Algarra Goosman B.Sc., M.Sc. (psychologist).
Last Update: 03/15/2022