
Get Answers from Clínica Tambre
There are several causes that can cause us not to ovulate. One of the most common is Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, a benign condition that affects many young women. It consists of an endocrine disorder that does not allow correct ovulation.
There could also be anovulation of hypothalamic or pituitary cause, such as intense physical exercise, low weight, etcetera. Other hormonal alterations such as alterations in thyroid hormone (TSH) or prolactin, can cause ovulation not to occur properly.

Advanced age would also be a cause why, in spite of having periods, in many cycles ovulation does not occur regularly.
It is normal for some doubts to arise at that time between the embryo transfer and the pregnancy test. In general, we recommend trying to lead as normal a life as possible, following some recommendations, but trying to be as calm and relaxed as possible.
In the case of starting with cold symptoms, such as coughing and sneezing, it will not affect the implantation or the chances of achieving pregnancy. However, according to studies, in case of high fever, it can affect to a greater or lesser extent depending on the degree of temperature elevation, its duration and the stage of development of the embryo in which it occurs, and can range from not affecting implantation failure or early miscarriage.
Hyperthermia is not part of the side effects of hormonal medication or embryo implantation, so in case of suffering it, it is best to see your doctor to find out if it is an infection and put the appropriate treatment for it; as well as taking antipyretics such as paracetamol or perform physical measures in order to reduce body temperature and improve the symptomatology. Remember that in pregnancy there are certain medications that should be avoided, so the ideal is not to self-medicate and consult your doctor whenever you need it.
Jana Bechthold, gynaecologist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, talks about the importance of psychological support in assisted reproduction treatments:
A reproductive treatment can be emotional, stressful and some patients even suffer from anxiety or depression, so it is very important to have a good psychological support. We know that also mental health is related or connected to fertility, so we know that a good psychological support can even increase the fertility rates.
The most important thing to perform a MACs technique is the sperm concentration, as well as the fluidity of the semen sample.
Esther Marbán, a gynaecologist specialising in fertility at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, tells us about reproductive options for women who do not have a male partner:
Well, everything will depend on her age. If the patient is young we normally recommend undergoing IUI, which means intrauterine insemination with a sperm donor. She can also undergo IVF (in vitro fertilization) and, of course, we also offer egg donation plus sperm donor. In some patients is also possible to do what we call embryo adoption, so the patient may adopt an embryo that has been previously created.
Esther Marbán, a gynaecologist specialising in fertility at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, tells us if there is any difference in the performance of the techniques in single motherhood:
Of course, everything will depend on the technique the patient is using. So, if we are talking about intrauterine insemination, we just need to give a small amount of medication normally to make one follicle or even two follicles grow in the patient's ovaries. Then, when the follicles are ready to ovulate, we prepare the sperm sample at the laboratory to introduce a small amount of that sample in the uterus. However, if we are talking about IVF, the process is like more complicated in terms of first we need to stimulate the patient's ovaries, then we need to retrieve those eggs (that will be fertilized at the laboratory with the donor sperm sample) and then we wait for 5 days to check how the embryos develop. Depending on the last decision of the patient in terms of checking the embryos before transferring them, the patient will need to do the embryo transfer or, if she decides to check the embryos before doing the embryo transfer, we won't do the embryo transfer at that moment and the embryos will be checked first and then, if there are healthy embryos to transfer, we will do the embryo the embryo transfer afterwards. However and finally, if we are talking about embryo adoption or egg donation treatment, the patient doesn't need to have the ovaries stimulated, we will just do a preparation of the uterus with the aim of having that uterus in the best conditions. Then, the egg donor (in case she is undergoing an egg donation treatment) will do the ovarian stimulation. As soon as we have the eggs and the embryos ready, the patient will undergo the embryo transfer. So, it's much easier treatment for them.
Esther Marbán, a gynaecologist specialising in fertility at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, tells us how sperm donors are chosen for single women:
Well, according to the spanish reprodution law, all donors (including male and female donors) should look like the patient. I mean, so we look for the most suitable donor for each patient. We do the selection in two different steps. In the first one, we consider the blood type, skin color, hair color, eye color... like the most general characteristics. And then, after having selected the most suitable donors, we use a special technology, called Fenomatch, that will do a facial biometry in terms of finding the most suitable donor for each patient and the perfect match.
Esther Marbán, a gynaecologist specialising in fertility at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, tells us whether the baby will resemble the mother in a single motherhood:
Well, everything will depend on the kind of treatment the patient is undergoing. I mean, if the patient is using her eggs, of course the baby will be like more similar to the patient. If the patient is undergoing a different treatment, of course we will also try to find the perfect donor for each patient, but it would be a different treatment and, of course, the chances of having a a very similar baby could be decreased because of that. But, in the end, as I mentioned, first we try to do our best in finding the best donor for each patient and, apart from that, there's something that which is called epigenetics, that are the small changes the DNA may have in the patients uterus, that can also make that the baby could be also quite similar to her mother. So, in the end, there are like different biological processes by which the the baby can be similar to the mother.
Esther Marbán, a gynaecologist specialising in fertility at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, tells us whether the number of single women resorting to assisted reproduction has increased:
Well, it's true that, according to our data, I would say that it's day by day more frequent to find patients that decide to become mothers on their own. And I would say that maybe in the last year we have seen like a slight increase in that kind of treatments.
Jana Bechthold, gynaecologist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, answers us in this video:
There is no medical indication to do a PGD in women that are younger than 35 years old because, statistically, most of the eggs of these women and their embryos should be chromosomic normal. However, there are certain reasons to perform a PGD in these women, which could be: implantation failure, repeated miscarriages or a male factor and also certain genetic diseases
Laura García de Miguel, medical director and fertility specialist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, tells us in this video what does artificial insemination by donor consist of:
This is a treatment that we can use with natural cycle or medication artificial with trying to stimulate a little bit follicles and we place the sperm in the uterus in the correct moment after having a concentrate sperm of the donor and having the maximus probabilities on that cycle to have a baby.
Laura García de Miguel, medical director and fertility specialist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, tells us about the differences between donor sperm insemination and partner sperm insemination:
In terms of stimulation or follow-up before the trigger there is no many difference between IUI with donor or IUI with a couple, with their partners. So it's more to do with... it's the same protocol, it's the same medication, it's the same follow-up during scans and it's only the difference if the sample comes from a donor or a partner.
Laura García de Miguel, medical director and fertility specialist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, talks about the duration of artificial insemination with donor sperm:
The treatment normally takes around 10 to 12 days and it really depends on the length of the cycle of the ovulation. So, if we use gonadotropins with low dosage (like 50 units or 75 international units) normally we have around 9 days to have a good follicle (around 18 or 20 millimeters) and be able to do the trigger with Ovitrelle with paroxetine medication and two days after, 36 hours after, we do the IUI. So, in total, it's 12 to 14 days maximum.
Laura García de Miguel, medical director and fertility specialist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, tells us in this video if there are any risks such as side effects or infections:
For all treatments there's always a risk. So, of course, the main risk is infections during the process, because we manipulate the uterus and we introduce a catheter, but the probability it's nearly zero percent. For the secondary effects of the medication it's very unlikely because it's low dosage of medication, but you could have headache or cramps... but it's very well tolerated.
Jana Bechthold, gynaecologist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, answers us in this video:
A timed intercourse has less success rates than an IUI, an intrauterine insemination. So couples that did, for example, three attempts of timed intercourse without success, in this cupboard is recommended to do an IUI. Also factors like problems with the ovulation or mild male factors. In this cases it's better to do directly an IUI
Sperm agglutination may be a reflection of a possible immunological factor, observing the presence of spermatozoa joined together somewhere in their structure (head, intermediate segment or tail). The presence of this phenomenon is usually related to a decrease in fertility.
The male history of spermatozoa should be taken into account in the assessment, such as obstruction of the seminal tract, vasovasostomies or bacterial suspicion. The presence of antisperm antibodies in patients diagnosed with oligozoospermia may reflect the presence of unilateral obstruction of a seminal duct. The presence of such antibodies in infertile patients may be associated with chlamydial and mycoplasmal infections.
Esther Marbán, fertility specialist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, tells us in this video about in vitro fertilisation (IVF) with frozen eggs:
his is the procedure by which we are going to defrost the eggs that the patient frozed in the past with the idea of creating the embryos. So, those cells will be fertilized with the patient's partner sample (or with a sperm donor sample) to create the embryos at the laboratory for a future embryo transfer.
T
Esther Marbán, fertility specialist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, talks to us about the pregnancy rate of IVF with the patient's own eggs:
Well, as we were mentioning before, the results will be different depending on the age the patient decided to freeze their eggs. If the patient frozes her eggs when she was young the result will be better, but if she's doing the treatment when she is in her 40s, the result will be almost the same if she's doing the treatment with fresh eggs at that moment or with frozen eggs that she has a froze at that moment also.
Esther Marbán, fertility specialist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, explains the IVF process with cryopreserved eggs:
The procedure is exactly the same. So, we will fertilize the eggs (that will be previously defrost at the laboratory), we will create the embryos and, depending on the treatment the patient wants to undergo, we will decide if we can do the embryo transfer with a fresh embryo or not. What we normally do is, if the patient agrees in doing the first embryo transfer with a fresh embryo, the patient should undergo a treatment to prepare the uterus to have it in the best conditions possible. After that procedure, we will defrost the eggs, they will be fertilized and the embryos (that will be created at the laboratory) we will select the best quality embryo to the embryo transfer. However, if the patient prefers to undergo what we call the pre-implantational genetic screening, she doesn't need to start her preparation until the embryos are ready. So, we defrost the eggs, we create the embryos and we do a small biopsy on the embryos to check them in terms of the chromosomes. After having suitable embryos to be transferred, the patient will start her preparation to transfer that embryo.
Esther Marbán, fertility specialist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, explains when egg vitrification is indicated before IVF treatment:
Well, according to Clinica Tambre statement, I can tell you that the majority of patients that decide to come to our clinic to do egg freezing is because of social reasons. So, many patients prefer to postpone their wish of becoming mother for some years and they prefer to freeze their eggs because they know that the result will be much better. Of course, some other patients may decide or may need to do that treatment because they are going to undergo maybe treatments that will be toxic for the ovaries and, in the end, they know that it can also affect the future fertility, so because of that they prefer to also freeze their eggs. But I would say that almost 90 percent of our patients decide to do it because of social problems.
Esther Marbán, fertility specialist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, talks to us about the benefits of IVF with vitrified eggs:
Well, everything will depend on the age when the patient decides to freeze their eggs. If she has come in a good age, I mean when they are young, they will be so much better. It means that we would need a lower number of eggs to have a positive outcome. So, if the patient is young, the quality is supposed to be also better. So, because of that, we recommend patients to come if possible if they are younger than 35 years old.
On some occasions, before performing an assisted reproduction technique, especially in vitro fertilisation, the gynaecologist prescribes a contraceptive pill from the first days of the period of the previous cycle.
In the event that the patient requires antibiotic treatment during the same period, due to a bacterial infection, it is common for the woman to be concerned about whether there is an interaction between the two drugs that could harm the effectiveness of her reproductive treatment. However, for most commonly used antibiotics, there is no solid scientific evidence to show a reduction in the efficacy of hormonal contraceptives, with one exception, rifamycin such as rifampicin or rifabutin, commonly used in the treatment of tuberculosis.
In any case, as I mentioned before, before starting the IVF cycle we will always check beforehand that it is the right time to start, so if the antibiotic has influenced the absorption of the contraceptives, we would detect it before starting the IVF cycle.
Jana Bechthold, gynaecologist at the Tambre clinic in Madrid, answers us in this video:
It is recommended to wait at least one year after giving birth for the next embryo transfer. The World Health Organization even recommends two years, especially if the woman had a cesarean section it is necessary to wait at least one year.
A serodiscordant couple is defined as a couple where one partner has a communicable infectious disease such as HIV and the other does not. It can also apply to other diseases such as hepatitis C and hepatitis B.
In cases where the male partner has the disease, the main way to eliminate the risk of infection is to perform a seminal lavage. The semen is processed in the laboratory, the semen is washed and a fraction is sent to confirm by molecular biology techniques that there are no traces of infection in the sample. If this is the case, the sample, which will remain frozen, can be used safely for subsequent treatment.
If the woman is the carrier of the infection, it is important that she has an undetectable or low viral load before starting treatment. In cases with a high viral load, it is recommended that the relevant treatment be carried out before the assisted reproduction treatment, in order to reduce the presence of the virus as much as possible and thus the risk of transmission to the child. Likewise, if treatment is required during pregnancy, it must be appropriately adjusted and approved for pregnancy by the specialist who is following the patient. In this situation of adequate treatment and undetectable viral load, the risk of transmitting the infection to the foetus is very low.
Yes, the truth is that nowadays, the antimullerian test and the antral follicle count are the most widely used and most reliable tests of ovarian reserve. There is a good correlation between them.
It is not ideal. It would be advisable to do it before any assisted reproduction technique. It is true that if you are carriers of the same disease, then when doing the biopsy of the embryos we can see the ones that are not altered.
Patients who undergo ovarian stimulation usually retain more fluid, as well as increase the volume of their ovaries.
In artificial insemination treatments there is usually no weight gain.
However, in vitro fertilization there is. Although the response is variable, given that the medications and doses can be different, in ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization there is usually an average weight increase of 1 kilo. This increase is transitory and usually decreases at the end of the cycle (as soon as menstruation stops if the treatment has not worked).
Indeed, it is possible that after having vitrified oocytes, the patient may not want to use them to obtain a pregnancy. After all, vitrification of oocytes allows us to postpone the decision to become a mother with your own eggs and have the peace of mind that when that time comes, you have the same chances of getting pregnant as you have at the moment.
However, it may happen that in the end you do not need to resort to an assisted reproduction technique to achieve it and you get pregnant naturally.
Depending on the laws in your partiular country or state, there are three options for the destination of the vitrified oocytes in addition to their own use:
- Donation of the egg cells for scientific research.
- Donation of the egg cells for use in reproductive techniques in other patients.
- Apply for the termination of the preservation.

In any case, if you meet the criteria, you will choose the purpose of your eggs. Another possibility is that you want to keep the vitrified eggs for a second gestation and thus complete your desired family project. Remember that once the oocytes are vitrified, they do not deteriorate with the passage of time, remaining in exactly the same conditions as when they were vitrified.
In artificial insemination (AI) it is important to know the ideal moment to perform the insemination, that is, to place the semen in the uterus.
For this it is essential to do ultrasound controls to control the size of the follicle. In the case of elongated follicles, two diameter measurements are always taken to see the real size of the follicle in order to know at what moment to induce the ovulation externally, with the administration of ovitrelle.
The moment when the dominant follicle reaches about 17 mm is usually on day 9 of the stimulation cycle, but there are women who reach the size of 17 before or after. That is why it is so important to do ultrasound controls every 48 hours.
Hormone analysis provides a lot of information to study fertility. It is advisable to look at the ovarian reserve in women over 35 years of age, or those with irregular menstrual cycles, previous ovarian surgery, oncology patients, etc.
In addition, the analysis of FSH, LH, estradiol, prolactin and progesterone provides valuable information for the study of fertility.
Pregnancy tests determine the presence of the hormone (beta-hCG= human beta chorionic gonadotropin) in the urine. This is produced when pregnancy occurs. A positive test means that this hormone is present in the urine and therefore the woman is pregnant.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is when the ovaries produce higher than normal amounts of androgens and this can interfere with the development and release of the egg. Sometimes, instead of eggs forming and maturing, cysts develop in the ovaries. Instead of the egg being released during ovulation, as it is in a normal menstrual cycle, the cysts grow and increase in size.
Only in the case of a cyst that produces hCG, which is very rare, the hormone would show in your urine and give a false-positive result with the pregnancy test.
Necrozoospermia is not related to inccorect implantation of the gestational sac outside the uterus, but is associated with IVF failure, poor seminal quality, poor prognosis for fertilization and creating embryos.
When giving advice in medicine, we must always individualize each case and bear in mind the various factors, above all because this illness is usually diagnosed more frequently in women, often of a reproductive age, and usually creates doubts and fears with respect to maternity.
The fundamental message to get across to women who suffer from this chronic autoimmune disease, is that if they wish, they can become mothers. Arthritis does not cause infertility nor reduces the likelyhood of falling pregnant; however, it can influence the decision of using certain drugs to control the disease, namely those which can affect the baby if she becomes pregnant during, or in the months following, treatment with the medication.
As such, it is very important for these women to receive multidisciplinary management, with rheumatologists, obstetricians, neonatologists and experts in assisted reproduction to have a global focus on the illness while considering the control of the patient´s symptoms, her quality of life and her desire to become a mother. If the use of gonadotoxins is deemed necessary, which can affect the quality and quantity of egg cells, reducing the ovarian reserve, and / or when we recommend delaying motherhood, vitrifying eggs beforehand, thus preserving fertility, will increase the chances of achieving a healthy pregnancy in the future.
Exactly. The recommendation of the Spanish Fertility Society (SEF) is to perform a genetic analysis on all donors. In this way, the most suitable donors can be chosen for each type of patient.
Transtubal transfer is no longer used, since the highest pregnancy rate is achieved with intrauterine embryo transfer.
In the past, ZIFT was a technique that was performed, but its results are not as good as in utero transfer. Likewise, it is a more invasive technique, since it requires sedation of the patient and is performed laparoscopically.
Currently, embryos can be transferred at day 5 (blastocyst), the maximum that technology allows today.
Embryonic blockage is the term used to refer to the fact that the embryos have not been able to form a blastocyst. They are normally embryos that usually stop developing on day +3/4 at the cell/morula stage.
Approximately between 50-60% of the embryos have the capacity to reach the blastocyst, the embryos that do not achieve this suffer the so-called embryonic arrest. Poor oocyte and seminal quality can be a reason for blocking the embryos. For example, it has been seen that sperm DNA fragmentation has a negative effect on embryonic development, producing a slower evolution of the embryos and being negatively related to embryonic arrest.
Another factor to take into account is the age of the oocyte. We know that the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the oocyte increases with the age of the woman, influencing the embryonic genetic load and therefore its development. In addition, there are studies that show that one of the main causes of embryonic arrest is the presence of chromosomal abnormalities in the cells of the embryo. Specifically, it has been seen that almost 70% of the embryos that do not form the blastocyst have chromosomal abnormalities.
Advances and new technologies have allowed embryos to be cultured up to day +6 of embryonic development. The long culture allows us to select the embryos that have the capacity to form the blastocyst on day +5/+6 and, therefore, allows us a better embryonic selection. It will not be until day +3 of the culture when the embryo activates the embryonic genome, this activation is essential for the embryos to reach the blastocyst stage.
In artificial insemination cycles it is not usually necessary to prepare the endometrium separately since, thanks to the secretion of estrogens by the ovaries, they will act on the endometrium causing its gradual growth.
In a small group of patients, it may happen that this synchronous endometrial development does not occur and that, when performing routine ultrasound controls during the cycle, we find that the endometrium is not growing as it should. These patients may benefit from low doses of estrogens during the end of ovarian stimulation to externally support endometrial growth.
In most instances 2 to 4 mg of oral or vaginal estrogens are sufficient to achieve adequate thickness. Also, all patients will use progesterone after insemination to promote implantation.
No, ovarian stimulation causes follicles to grow that would not naturally grow, but it does not accelerate the rate of follicle or egg loss.
In a woman's normal cycle, a follicle is selected to be the one chosen for ovulation. Along with that selected follicle, a cohort of follicles that are not chosen will be lost after ovulation.
In ovarian stimulation, this cohort of pre-selected follicles is used so that they grow and more eggs can be obtained than are produced naturally and thus have a greater yield of the assisted reproduction technique.
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is a glycoprotein hormone produced both by the embryo and by the syncytiotrophoblast, a part of the placenta. The function of this hormone is to ensure that the embryo receives the nutritional and hormonal factors and protection necessary for its proper development.
In most sperm banks it is possible to reserve doses of donor sperm for successive pregnancies in order to have biological siblings. The number of doses to reserve will depend on the type of treatment.
This reservation can be made as long as the availability of donor sperm doses is verified and the donor has not reached the number of newborns allowed by the Spanish assisted reproduction law (a maximum of 6 children).
Gonadotropins are hormones that are used primarily to stimulate the ovaries, and eventually to stimulate sperm production in males.
In women who need to undergo assisted reproduction treatment to become pregnant, either artificial insemination or in vitro fertilization, gonadotropins are needed to stimulate the growth of eggs.
Gonadotropins are hormones that are administered by subcutaneous injections and are administered by the patient herself with the help of very easy-to-use devices. Depending on the treatment and the particular case, the physician will choose the appropriate doses of gonadotropins.
The side effects of these hormones are usually emotional lability and mood swings, headache and in the last days of the treatments abdominal distension and menstrual-like sensations.
It is very important to use gonadotropins only under medical prescription, with ultrasound controls to evaluate the response of follicles in the ovaries and to indicate the days to be administered and the dose.
Nowadays, in the case of a male with suboptimal semen quality due to idiopathic causes, we recommend correcting habits, trying to improve the diet by being more balanced and limiting animal fat, and getting at least 7 hours of sleep. In addition, physical exercise should be done on a regular basis but it should not be strenuous exercise, as competitive sports have been shown to cause physical stress that decreases semen quality. We add a dietary supplement that includes at least L-carnitine, Coenzyme Q-10 and omega 3-6 fatty acids. This treatment should be maintained for at least 3 months so that at least one cycle of spermatogenesis (62-75 days) is affected by this treatment, and desirably until pregnancy is achieved.
There are certain signs that may suggest that a woman is not fertile. The first sign is if we have irregular periods or no periods at all. In this case, it is very important to go to the gynecologist to assess the cause of irregular cycles, and discuss the possible impact on fertility, to see if it is advisable, for example, to perform an egg freezing.
There may also be other signs such as very painful periods, dysmenorrhea, which could be associated with endometriosis. In the case of a patient with endometriosis, it is necessary to have regular check-ups with a gynecologist to assess possible treatments and evaluate the ovarian reserve.
In addition, in women who have had pelvic surgeries, or who have fibroids, it is necessary to make a consultation of the possible impact of these processes on future fertility.
On the other hand, in patients with endocrine disorders such as overweight or obesity, thyroid disorders, it is highly advisable to talk to the specialist to assess possible hormonal alterations that may affect the chances of pregnancy.
Finally, those patients who have hirsutism or very marked acne, may also be associated with ovarian hormone alterations that may decrease fertility.
It is very common to go to a first fertility visit after having visited other centres. If you have had tests done at another clinic or have had previous fertility treatments, it is highly recommended that you bring all the reports with you.
The gynaecologist who is an expert in reproduction will be able to know your case in more detail and draw up a better diagnosis and detailed plan if he/she assesses all the tests or reports carried out during the first consultation.
The tests that we consider to be up to date are those less than a year old, but when in doubt it is better to bring everything that has been done previously.
Antioxidants can decrease oxidative stress and thus help to improve sperm quality.
Oxidative stress can affect sperm quality, both by damaging sperm motility and by fragmenting DNA, whereby the genetic alteration can be passed on to the embryo. The most important thing to improve sperm quality is to have a healthy lifestyle.
No, ovulation induction is the process by which the growth of 1 or several follicles of the ovary is produced thanks to the administration of drugs called Gonadotropins. After this, ovulation is usually triggered in a controlled manner.
Once this ovulation induction has been performed, intercourse can be programmed, that is to say, the couple can be told when ovulation will occur approximately and when they should have sexual intercourse to increase the chances of pregnancy.
In the treatment of frozen embryos, oocyte or embryo donation, when carried out in a substituted cycle (with medication) the hormonal secretion of the ovary must be simulated. In this way, treatment is initiated with the patient's period and estrogens are added in tablets or patches to promote endometrial growth. Normally, a control ultrasound is performed after 10-12 days to check this growth. If the appearance is trilaminar and the thickness is above 7-8 mm, the endometrium is considered to be ready for the embryo transfer. For this, progesterone should be added as many days before the embryo to be transferred. Both hormones (estrogen and progesterone) must be maintained at least until the day of the pregnancy test and if it is positive, the first weeks of gestation will be maintained.
Estrogens are the hormones produced by ovaries. A very low level of estrogen is usually found in a case of non-functioning ovaries (in cases of ovarian failure, menopause, etc.). The consequences of having a very low level of estrogen are the same as during menopause (vaginal dryness, decreased libido, etc.).
In a woman's normal menstrual cycle, for two or three days there is a low level of oestrogen (the first few days of menstruation) but the oestrogens quickly start to rise, until they reach a maximum, when ovulation occurs.
Ovarian insufficiency or ovarian failure is the condition suffered by young women, under 42 years, with malfunction of the ovary due to low ovarian reserve.
All women lose proper ovarian function at some point in their lives, since the ovary is endowed with follicles (which inside have eggs) that are going to decrease throughout our lives, and are not going to regenerate again.
If exhaustion comes at 48 years, it is not a problem, and menopause occurs naturally.
However, in other women, there may be ovarian depletion at a young age. If it is accompanied by alterations in the pattern of the menstruational cycles, an early ovarian failure will occur. If, on the other hand, there are no alterations in the menstrual pattern, it will be called occult ovarian failure.
Women who have hypothyroidism suffer from a slowdown in the production of hormones by the thyroid gland.
In these women, it is necessary, regardless of the technique used (fertilization in vitro, ovodonation), to correct with thyroid hormone (oral tablets) until a good TSH is obtained, below 2.5 (thyroid hormone) to guarantee that the implantation can be produced without problems.
This treatment will continue until pregnancy and it is important to make periodic controls with the endocrinologist to evaluate if it is necessary to increase or decrease the doses of the treatment.
Pelvic inflammatory disease is a pathology that is diagnosed by the presence of clinical compatible with it: fever, pelvic pain and the finding in the cervical culture or culture of endometrial aspirate bacteria that produce this pathology, such as gonococcus or chlamydia, among other things.
The most sensitive diagnostic test is laparoscopy, but in the vast majority of cases the diagnosis of pelvic inflammatory disease is made without having to resort to it. Blood tests are performed to determine the degree of infection, leukocytosis, as well as cultures with swabbing to detect bacteria that may cause this disease.
The duration of artificial insemination is usually about 5 minutes if there is no problem. After the process, the patient will rest for 20-30 minutes and then leave the clinic with the instructions until the day of the pregnancy test.
Rest after insemination is not obligatory, as no evidence exists that it improves the pregnancy rate.
Sterility caused by anabolic steroids in women is specifically due to the effect of androgen on the ovary causing anovulation and a picture similar to polycystic ovary syndrome. Its effect can be reversed after a while. Let us remember that cases of gestation have been described even in women who had been treated with male hormones to change sex.
We speak of Infertility of Unknown Origin (DOE) when after the basic study of infertility there is no cause that justifies reproductive failure. The basic infertility study does not attempt to analyse each of the events or organs that determine fertility. It is not a question of identifying what does not work in a person, but of establishing whether the minimum conditions are in place to be able to start a couple's reproduction treatment. In other words, it is a question of establishing a therapeutic strategy. The basic studies are therefore aimed at determining whether there is:
- Adequate ovarian reserve in the woman
- Affectation of seminal quality in men
- Tubal alteration
- Uterine factor
Ideally, treatment of vaginismus should be the solution to the couple's "sterility problem". Once sexual dysfunction has been overcome, pregnancy can be achieved naturally.
Vaginismus treatments are often long, which can conflict with the desire for motherhood, especially in cases where age or ovarian reserve are in limit ranges. In cases of this type, we may find ourselves in the need to start reproductive treatments directly. These range from vaginal insemination of the semen sample at the time of ovulation, a technique that does not require medical assistance if the woman is able to self-inoculate the sample, to more complex reproduction techniques. Self-insemination can be the first step for young couples with no known pathology. At older ages, the relevance of carrying out sterility tests and reproduction treatments will be evaluated in each case.
With fertilization, the meiosis of the oocyte is completed (reducing division that allows the reduction of chromosomes by half), this is evidenced by the appearance of a small satellite structure called the 2nd polar corpuscle. In addition, two intracellular structures are formed, the pronuclei, which contain genetic information of each of the parents. The appearance of the pronuclei allows us to determine whether or not there has been fertilization and if this has been anomalous in which case the embryo would not be selected. These structures are visible for a few hours, so classically, it was necessary to organize the activity of the IVF laboratories to be able to evaluate the possibility of fertilization within very specific hours. If the assessment was not made at the right time, it could lead to diagnostic errors. The use of Time-Lapse systems, incubators with video systems that allow the evolution of embryos to be recorded, has allowed these practices to be modified. In such a way that currently, with morphokinetic incubators (GERI; Embryoscope...), embryologists review the images and can evaluate whether fertilization has taken place, has been correct and at what time it has taken place. In this way an ideal evaluation of the embryo is achieved.
The triple test or triple screen is a universal test that is done in all women when they are pregnant, particularly around week 12 of pregnancy. It pays special attention to the risk of Down's syndrome in the fetus by combining two markers from the first trimester ultrasound with two hormones examined in pregnant women (BHCG + AFP) along with her age.
In case your OB/GYN refers you directly to invasive tests (amnio test or chorionic villus sampling) because you've been pregnant before and chromosomal abnormalities were detected in the fetus, then a triple test would be unnecessary.
ICSI or Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection is a type of In Vitro Fertilization that is used to fertilize the egg cell. With ICSI, the sperm cell is selected and injected within each one of the eggs collected.
Unanimously recognized indications of ICSI include:
- Severe male infertility: a single sperm per egg cell is enough
- Previous fertilization failure using conventional IVF
- Issues with the oocytes: poor-quality eggs may compromise sperm penetration into the egg cell
- Techniques that involve isolating the egg from the cells that surround it (egg donation, preimplantation diagnosis...)
The number of embryos to transfer to a patient is not dependent on the technique performed for the genetic analysis of embryos, but on the stage, quality, and particularities of each patient. Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis is usually performed in cases of advanced maternal age (aneuploidy screening) or when there exist severe genetic pathologies (in many cases, present in the woman). In both situations, a multiple pregnancy would be contraindicated.
So, given all these circumstances, doctors usually recommend Single Embryo Transfers (SETs).
The treatment to follow varies depending on whether it is a fresh embryo transfer (after an IVF cycle) or a frozen embryo transfer.
With fresh embryos, patients follow a hormonal treatment based on applying injections to stimulate the ovaries during 10 days approximately. After retrieving the eggs, the patient starts taking progesterone vaginally or subcutaneosly.
With frozen embryos, patients have to prepare during 2 weeks with estrogens (in patches or tablets). Depending on the day of the embryo transfer, progesterone may be prescribed as well. In some cases, the patient follows a natural cycle, without using estrogens.
Seminal quality can also be evaluated by studying the genetic content of spermatozoa. First, we can study DNA integrity, which is fundamental to obtain correct embryonic development. However, sometimes it is fragmented. The fragmentation test evaluates the percentage of fragmented spermatozoa in the ejaculate.
On the other hand, we can study if the sperm have a correct chromosomal content through the FISH study (5 pairs of chromosomes are evaluated) or Chromosperm (a general chromosomal profile is evaluated). An ejaculate with a high percentage of chromosomally altered sperm could generate a greater number of aneuploid embryos.
Hydrocele is the accumulation of fluid between one of the layers of the testicle (vaginal tunic) and the scrotum of one or both testicles. It can be congenital (affects babies at birth) or acquired, i.e. secondary to infections, trauma, tumors, surgeries on the testicle, etc.
In most cases the hydrocele is presented as an inflammation of the testicle, not painful or causing mild discomfort. In itself, it is not a cause of sterility but certain cases, such as those caused by an infection, can reduce the reproductive capacity.
There are no concrete actions to increase sperm volume. The right thing would be to redirect the question towards: how can semen quality be improved?
Seminal characteristics are specific to each male. However, there are certain factors that can modify the quality of the semen, causing it to increase or decrease.
Factors that diminish seminal quality are: tobacco, alcohol, drugs, a bad diet, a very stressful life rhythm, continuous and direct exposure to radiation or chemical agents harmful to health.
In order to improve seminal quality the right thing is to lead a healthy way of life:
- Balanced and healthy food (encourage the regular consumption of foods rich in antioxidants)
- Maintain an adequate weight (excess weight is negative for seminal quality)
- Maintain a low-moderate stress level
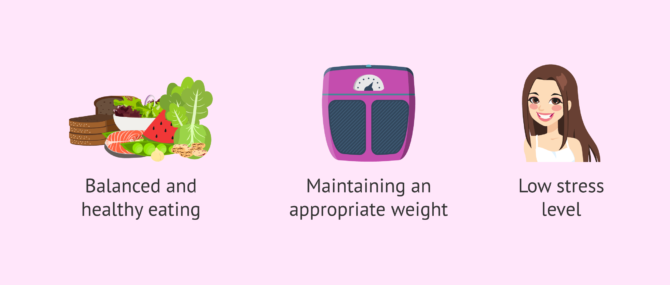
However, there are pathologies such as agenesis of vas deferens, infections in glands such as seminal vesicles or prostate, etc. that can reduce the volume of an ejaculate, and therefore it is very important to consult a specialist.
The number of embryos to be transferred to a patient does not depend on the technique that has been practiced on the embryo, but on the day it is found, its quality and the intrinsic characteristics of each patient. The performance of a Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis is associated in most cases with advanced maternal age (screening of aneuploidies) or the presence of serious genetic pathologies (in many cases present in the woman). In both cases, multiple pregnancy is contraindicated.
For all these circumstances, the medical advice is usually the transfer of a single embryo.